नोटिस बोर्ड
सभी घोषणाएँ
$0
Identity not verified

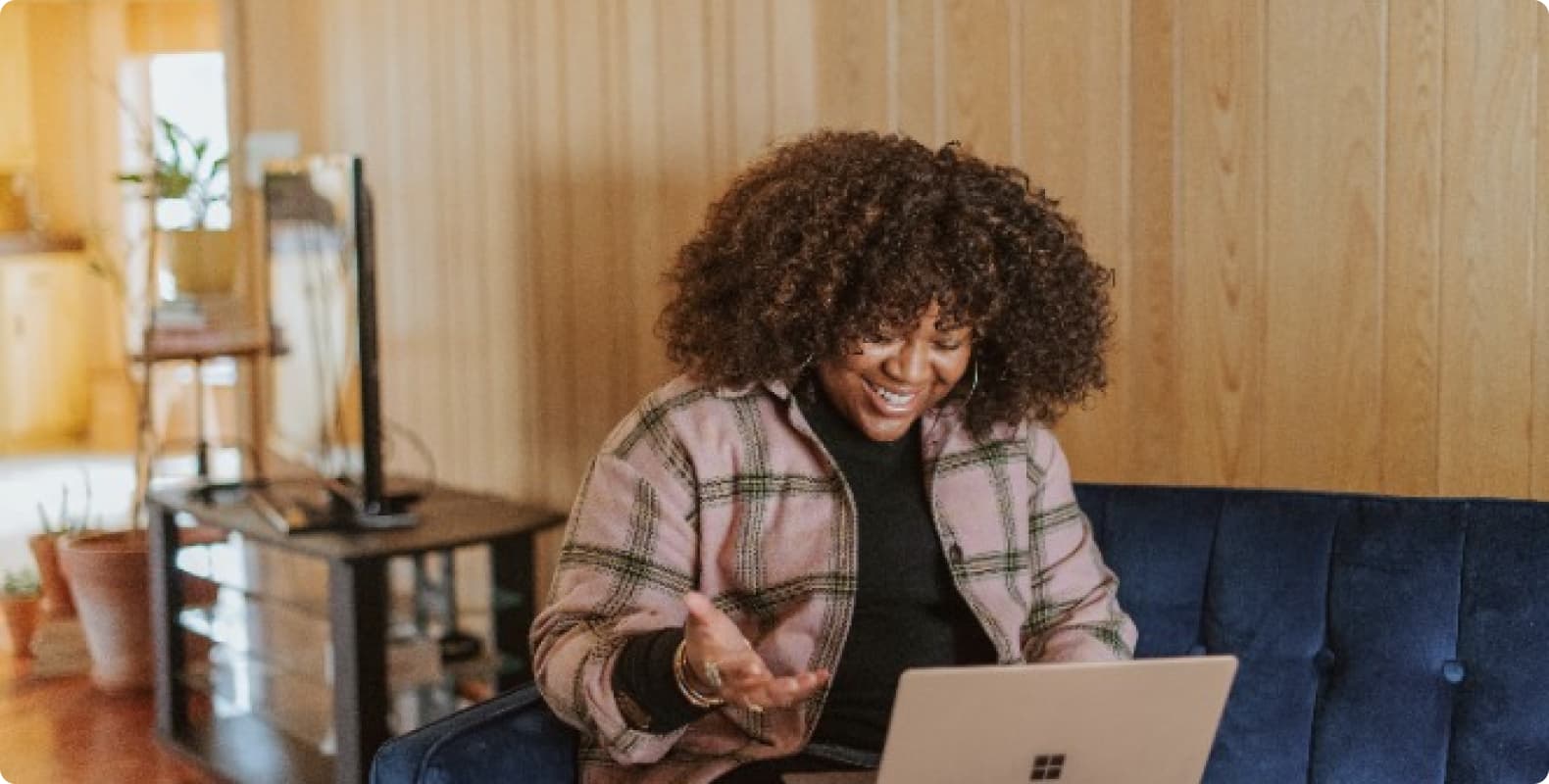
Dashboard

Local Time Zone

Use the device's local time zone
(UTC+0:00) Greenwich Mean Time
(UTC-8:00) Pacific Time (US & Canada)
(UTC-7:00) Arizona(US)
(UTC+8:00) Hong Kong(CN), Singapore

Account

My News
Ticket Center

Identity Authentication
Log Out

EN

नोटिस बोर्ड
सभी घोषणाएँ
$0
Identity not verified

Dashboard

Local Time Zone

Use the device's local time zone
(UTC+0:00) Greenwich Mean Time
(UTC-8:00) Pacific Time (US & Canada)
(UTC-7:00) Arizona(US)
(UTC+8:00) Hong Kong(CN), Singapore

Account

My News
Ticket Center

Identity Authentication
Log Out